Unless you’ve been living under a rock, you’ve probably heard that fish oil is good for pets and people.
These Omega 3 fatty acids are among the most studied supplements in existence, with thousands of studies backing their benefits. While most pet owners know they help with joint pain, that’s just scratching the surface.
Today I’ll share four little-known benefits of Omega 3s (and one bonus benefit I bet you didn’t know) that could make a significant difference for your pet’s health!
But first, a quick primer on what we’re actually talking about (hint: not all Omega 3s are created equal)…
The Kinky Backstory
It all starts with tiny single cell creatures adapting to life in the cold part of the ocean.
To keep their cells from freezing and getting too stiff, microalgae evolved to create Omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), specifically EPA and DHA. They are long chains of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, linked by bonds that make the structure kinky and bendy, rather than stiff and inflexible. They are essential compounds—mammals must eat them—that form the building blocks of lipids (fats) in membranes.
These kinky little microalgae do great against the cold, but end up getting eaten quite a lot.
The animals that eat them incorporate the omega-3 FA’s into their bodies. And on and on up the food chain.
Cold water fish like salmon and mackerel have quite high levels of the marine Omega 3’s because they eat lots of these small organisms in the cold water where they live. Plus they are quite fatty fish—incorporating lots of these fat building blocks into their bodies.
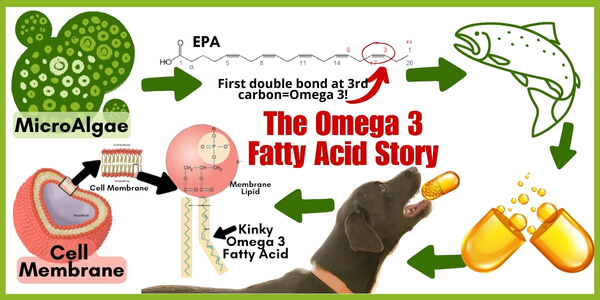
Fish oil supplements are EPA and DHA fatty acids, in concentrated form, from the fat of cold water fish. There are also marine algae and krill oil supplements that contain the same thing.
Simple right?
Not so fast.
Plants make Omega 3 fatty acids too. But they make ALA (alpha-linolenic acid)—not EPA or DHA—which has a similar structure but not anywhere near the amazing effects of the marine-derived Omega-3’s.
ALA can be converted in the body to the more useful forms, but unfortunately this process is terribly inefficient. Less than 5% gets converted in dogs, and essentially none in cats.
This means that adding flaxseed or chia seeds to a pet diet is pretty much useless (though it makes for a nice label on the bag that says added Omega 3 fatty acids).
Now we come to the kinky part… I know you were all waiting for that 
(hey, I’ve got to do something to keep you reading through the science bits!)
When the omega-3 fatty acids are eaten, they are incorporated into cell membranes, and it is this special kinked and bendy shape that creates more fluid and flexible cells that function optimally, especially in the brain, eye and heart.
And higher levels of omega 3’s in the diet, means more get put into cell membranes.
They don’t just sit in that cell membrane and call it a day though. When the body needs to generate an inflammatory response (or resolve one), the omega 3 fatty acids are released from the membrane and they are converted into signaling molecules.
And what signal do they send?
They tend to send “calm the heck down” signals to the inflammation pathways.
And we know from research that long-term, unchecked inflammation is very bad for the body and is at the heart of so many chronic life-threatening diseases.
But no backstory is complete without an enemy.
Omega 6 fatty acids, mostly from seed oils like corn, soybean, and sunflower, play the bad guy here. They are also PUFA’s, but their kink is just a little different.
The first double bond (double bonds between carbons create the bends) is at the 6th carbon, versus the 3rd (hence the name Omega 6 vs Omega 3), and this small variation leads to profound differences in effects. When the body has lots of those Omega 6’s in the cell membranes, they don’t function as well, and when they come out and get turned into signals, the signals ramp up inflammation.
The moral of this backstory?
It comes down to a numbers game.
The body doesn’t “prefer” to use Omega 3’s, or “choose” to put them in the membranes, over Omega 6’s. It will take what’s present in higher numbers and use it.
More omega 3’s around? More get used to create optimal cell function and anti-inflammatory signals than the pro-inflammatory Omega 6’s.
This is why consistent supplementation over weeks is important – it takes time to gradually shift those membrane compositions.
The Most Recommended Use:
Now that we understand how omega-3s work in the body, let’s look at their most well-known application before exploring the hidden benefits.
Anti-Inflammatory in Joints
They are the most commonly recommended supplement for osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis is long term wear and tear, plus inflammation inside of joints, that causes pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. EPA and DHA decrease inflammatory compounds that break down cartilage and trigger pain.
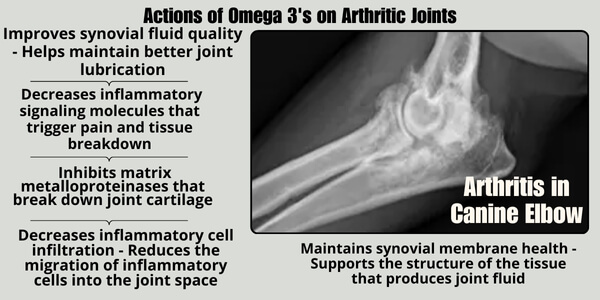
Research has shown that consistent omega-3 supplementation can significantly improve mobility and comfort in arthritic pets, with many showing visible improvement in their ability to climb stairs, jump, play, and enjoy daily activities. What makes omega-3s particularly valuable is that they address the underlying inflammation rather than just masking symptoms, potentially slowing the progression of joint damage over time.
But they do so much beyond helping sore joints. I will tell you about some lesser known benefits and effects that most people don’t know.
Surprising Benefits
The brain absolutely thrives on these guys.
In fact, DHA makes up about 40% of the PUFA’s in the brain, and even more in the retina- the eye’s special sensory layer.
1. Brain and Eye Development in Puppies and Kittens
DHA is critical during pregnancy, nursing, and the first year of life for puppies and kittens for optimal brain and vision development.

DHA:
- Builds better brain connections: Helps neurons connect properly as the brain develops
- Improves vision: Critical component in eye structures that develop during early life
- Speeds up nerve signals: Helps form the insulating covers around nerve fibers
- Enhances learning ability: Puppies with DHA supplements learn faster and are more trainable
- Supports brain adaptability: Helps the young brain form new connections during critical learning periods
-
Developing brains aren’t the only ones to benefit from DHA and EPA though.
2. Aging Brain Protection and Repair
Aging brains, those at risk from cognitive decline, can also benefit from Omega 3’s (EPA mostly).
They help to:
- Protect brain cells: Shields neurons from damage caused by age-related oxidative stress
- Maintain brain flexibility: Keeps cell membranes fluid when they would naturally become more rigid with age
- Reduce brain inflammation: Helps control inflammatory processes that increase with aging
- Preserve cognitive function: May slow mental decline and memory loss in senior pets
- Support mood balance: Helps regulate brain chemicals related to anxiety and well-being
- Improves blood flow: Enhances circulation to brain tissues, delivering more oxygen and nutrients
3. Skin Barrier Repair and Treatment for Itch and Inflammation
Did you know that Omega 3 fatty acids can be used to help treat itchy, inflamed skin?
Skin allergies are very common in dogs and cats, and are rarely cured, so long term strategies to decrease inflammation and rebuild damaged skin barriers are valuable.

Because itchy skin and secondary infections come back over and over again, management can seem never-ending, expensive and very frustrating for owners. Not to mention very uncomfortable for pets.
Omega 3 fatty acids:
- Strengthen skin’s moisture barrier
- Reduce inflammatory signals in allergic skin
- Decrease itch intensity
- Help skin recover faster from self-trauma caused by scratching
- Help regulate oil production in skin
- Support healthy skin cell turnover
- Improves coat quality and shine
These benefits aren’t seen until 6-8 weeks of consistent supplementation though.
4. Failing Kidney Protection
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) was one of the most heartbreaking conditions I faced regularly in my veterinary practice.

So many older cats suffered for years as the disease slowly progressed – they’d gradually lose weight, become weaker, feel increasingly ill, and eat less and less.
While we can’t cure CKD, we can significantly slow its progression.
Nutrition is a critical aspect of CKD management, with three well-studied interventions making a real difference.
Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation is one of these critical approaches. EPA and DHA can help protect kidney function and reduce disease progression by decreasing chronic inflammation and improving several clinical markers of kidney health. The other two nutritional cornerstones for managing CKD are phosphorus restriction to reduce mineral buildup and high-quality protein at appropriate levels to reduce toxic waste products that stressed kidneys struggle to filter while maintaining muscle mass.
Many veterinary renal diets already incorporate high levels of EPA and DHA which should be factored into your total supplementation calculations.
Should pet owners wait to supplement aging pets with Omega 3’s until kidney disease is diagnosed?
Let’s consider a few important facts:
- Approximately 30-40% of cats over age 10 develop kidney disease, while up to 15% of dogs are affected.
- Early diagnosis is extremely challenging. There is a critical window between the first loss of kidney function and the recognizable bloodwork changes we see, when Omega 3’s could be working to protect kidney function. Unfortunately, we often see the first abnormal blood changes when 75% of kidney function is already lost.
- Omega-3 supplementation is safe for most aging pets and provides multiple benefits beyond kidney protection – including joint, brain, heart, and skin health.
- The cost of supplementation is minimal compared to the treatments required for advanced kidney disease.
These simple facts highlight the importance of ensuring good levels of Omega 3’s for aging pets, particularly cats, rather than waiting until disease is diagnosed. This can be through supplements or a high-quality diet with good levels of omega-3 fatty acids.
I bet you didn’t know this last one!
Bonus: Decreased Need for Prescription Medications
One of the most valuable yet overlooked benefits of Omega-3 supplementation is its potential to reduce your pet’s need for prescription medications.
Multiple clinical studies have shown that consistent omega-3 supplementation can allow for reducing doses of:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs like carprofen or meloxicam) for arthritis, sometimes by up to 25%
- Steroids like prednisone for allergic skin conditions
- Medications used for kidney disease management and canine cognitive dysfunction
We know that medications can have side effects, so decreasing their use or dosage long term can potentially avoid problems.
It’s worth remembering that treating most pet health issues works best with a team approach. One single treatment rarely fixes everything, especially for complex conditions. Omega-3s, other supplements and diet changes work alongside conventional medications—they’re partners, not replacements.
You should never adjust your pet’s medication without veterinary guidance, but discussing omega-3 supplementation with your vet could lead to a more integrative approach that relies less heavily on pharmaceuticals. Many vets are happy to discuss how these supplements might help reduce the need for some medications or their dosages over time.
But wait, there’s more!
Research continues to uncover additional benefits of omega-3s for pets. We have studies showing benefits for heart health, seizure management, digestive and dental issues, cancer support, anxiety, and metabolic health. As science advances, we’re discovering that these remarkable fatty acids may benefit nearly every system in your pet’s body.
PUTTING THIS INTO ACTION
Now that you understand the powerful benefits of omega-3 fatty acids for your pet, here’s how to put this knowledge to work:
What To Do Next:
- Talk to your vet about appropriate omega-3 supplementation for your pet’s specific needs and health conditions
- Check your current pet food ingredients for marine-based omega-3 sources (fish oil, krill oil, algae) versus plant sources (flaxseed)
- Choose a high-quality supplement that comes in a dark bottle with added antioxidants to prevent rancidity
- Start with the appropriate dose based on your pet’s weight (see dosing guidelines in my free supplement guide)
- Be consistent – remember that it takes 6-8 weeks of daily supplementation to see noticeable benefits
- Store your supplements properly in a cool, dark place or refrigerate after opening
- Monitor your pet for improvements in mobility, skin condition, or cognitive function
Remember, small changes consistently applied can lead to significant improvements in your pet’s health and quality of life!

Download your free copy of my Quickstart Guide to the Top Supplements Every Pet Owner Should Know. I created this science-backed resource to help you navigate the most effective supplements for the top 4 reasons pets visit the vet:
- Osteoarthritis
- Anxiety
- Itchy Skin
- Gastrointestinal issues (vomiting and diarrhea)
This comprehensive guide includes:
- Clear explanations of each condition
- The top 3 research-backed supplements for each problem
- Plain-language descriptions of what each supplement is and how it works
- Practical tips on dosing and administration
- Recommended high-quality products you can trust
- Scientific references you can share with your veterinarian
Whether your pet is currently facing one of these issues or you want to be prepared for the future, this guide puts veterinary knowledge directly in your hands.